- Universal Access NumberWith this service customers who dial this number are automatically routed to the nearest open office or to an office with free lines. The difference between this service and the previous one is that the customer pays for the call.
- Premium Rate Service
The calls are charged at a rate higher than for normal calls. This service is used in connection with information services offered by service providers and could be for example, sports results, dating services, weather forecasts, horoscopes, etc. - Credit or Account Card Service
The user pays for the call using a normal credit card in a public telephone instead of using coins. - Universal Personal Telecommunication (UPT)
This service makes it possible for a subscriber to be reached on any telephone via the same number wherever he/she is located. Also, the subscriber can be charged on his/her own account from ANY phone he/she uses. - Televoting
This is a service where e.g. TV-viewers are asked to call in and register their opinion on an issue by calling to either one of two numbers (where one can mean 'YES' and the other one 'NO').
Current Position
Engineer- Carrier Business
Vodafone Essar Mobile Services, Delhi.
Ritesh Bansal
Professional Experience
Hi,
I am currently working with Vodafone Essar Mobile Services, Delhi as Engineer- Carrier Business where I have to do deal with Long Distance Services technically like World Calling Cards, Toll Free No's tariff configuration, server operations and mantainance etc.
Previously I had worked with Ericsson India Pvt. Ltd. as Engineer- Front Office (offroll) on Bharti Airtel Project as BSS-FS and IN-FS engineer performing fault management by coordinating support resources, managing technical escalation to ensure fault is rectified within agreed SLA’s & providing technical support to regional teams for O&M support.
I am currently working with Vodafone Essar Mobile Services, Delhi as Engineer- Carrier Business where I have to do deal with Long Distance Services technically like World Calling Cards, Toll Free No's tariff configuration, server operations and mantainance etc.
Previously I had worked with Ericsson India Pvt. Ltd. as Engineer- Front Office (offroll) on Bharti Airtel Project as BSS-FS and IN-FS engineer performing fault management by coordinating support resources, managing technical escalation to ensure fault is rectified within agreed SLA’s & providing technical support to regional teams for O&M support.
Educational Background
B.E in Electronics & Communication
AISSCE (12th) and AISSE (10th) from CBSE
AISSCE (12th) and AISSE (10th) from CBSE
Blog Archive
Monday, November 22, 2010
IN services
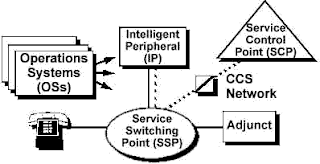
Architecture of IN
An IN infrastructure typically involves service logic on network platforms, an out-of-band signaling system, and IN-capable software in the network switch. With this infrastructure in place, service providers, end users and third parties can, in theory, create and modify services independently of switch vendors.
Intelligent Network : Introduction
IN has become one of the most critical technologies in the information industry because of its promise of quick service deployment, efficient network resource utilisation, vendor independence through standardisation, and the separation of intelligence and switching functionality. This essay gives a general description of IN technology and application.
An intelligent network (IN) is a service-independent telecommunications network. That is, intelligence is taken out of the switch and placed in computer nodes that are distributed throughout the network. This provides the network operator with the means to develop and control services more efficiently. New capabilities can be rapidly introduced into the network. Once introduced, services are easily customized to meet individual customer's needs. The orginal IN networks were introduced by BELLCORE organization in theUS Europe - began to develop it.
Intelligent Network systems enable service providers to differentiate themselves from their competitors, increase revenue, and enhance the quality and scope of services to their subscribers. Services may be customized for each user, and end users can control their service through reconfiguration via the telephone or PC workstation. Because Intelligent Network systems often comply with standard interfaces, service providers are less likely to find themselves locked into their suppliers.
The basic promise of the Intelligent Network is to separate the core intelligence and databases for controlling services from the switching elements
An intelligent network (IN) is a service-independent telecommunications network. That is, intelligence is taken out of the switch and placed in computer nodes that are distributed throughout the network. This provides the network operator with the means to develop and control services more efficiently. New capabilities can be rapidly introduced into the network. Once introduced, services are easily customized to meet individual customer's needs. The orginal IN networks were introduced by BELLCORE organization in the
Intelligent Network systems enable service providers to differentiate themselves from their competitors, increase revenue, and enhance the quality and scope of services to their subscribers. Services may be customized for each user, and end users can control their service through reconfiguration via the telephone or PC workstation. Because Intelligent Network systems often comply with standard interfaces, service providers are less likely to find themselves locked into their suppliers.
The basic promise of the Intelligent Network is to separate the core intelligence and databases for controlling services from the switching elements
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)